AI Specialist
|
This is the beginning of the complete workshop guide for AI Specialists. It includes step-by-step explanations, different approaches you can take to complete the workshop, and additional information to help you better understand the underlying technology and its business value. Following the full guide takes time. If you’re short on time or simply want a quick, copy-paste style guide to complete the workshop efficiently, I recommend using the quick guide available here. |
Background
You’ve been chosen as the lead AI specialist for ACME’s latest workplace safety initiative. The company is counting on your expertise to solve a critical challenge ensuring that every worker on the factory floor is equipped with proper safety gear. Hardhats are essential for preventing head injuries, but compliance isn’t always guaranteed. Now, it’s your responsibility to design the AI driven solution that could prevent the next accident.
Your mission is to develop an object detection system that monitors workers in real time, identifying whether they’re wearing hardhats as they approach machinery. The system will rely on existing USB webcams across the factory floor, feeding video streams into AI models deployed on industrial PCs (IPCs) equipped with NVIDIA GPUs. When someone enters a hazardous area without a hardhat, the model will trigger instant alerts, creating a digital safety net that supervisors can rely on.
To bring this vision to life, you’ll lead the entire AI development pipeline. From gathering raw video footage and labeling datasets to building and refining the object detection model, your work will shape the core of this safety solution. Fine tuning the model for accuracy and ensuring smooth deployment will require close collaboration with the DevOps and application development teams, aligning the AI model with the broader infrastructure ACME is deploying.
As you chart the path forward, you’re faced with key decisions about the best approach to object detection. Building a model from scratch is possible using frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch, but that route comes with significant demands extensive data collection, complex architecture design, and lengthy training cycles. While custom models offer flexibility, the potential for delays and increased costs makes this a less practical option for the project’s tight timelines.
Instead, you opt for a faster, more effective solution leveraging pre-trained models. Models like Faster R-CNN, SSD, and EfficientDet all offer compelling benefits, but for ACME’s needs, YOLO (You Only Look Once) stands out. Known for its unmatched speed and efficiency, YOLO delivers the performance necessary to detect workers on the move without missing critical details. Additionally, unlike traditional methods that involve separate steps for identifying objects and classifying them, YOLO accomplishes both tasks in a single pass.
Now, with YOLO selected as the foundation, the next steps are clear. You’ll begin collecting and curating the training data, refining the model, and preparing it for deployment on-site. Each step you take will help safeguard the workforce, ensuring that AI becomes a cornerstone of ACME’s commitment to safety.
Toolset
To successfully develop and deploy the hardhat detection AI system, the workshop will utilize a suite of powerful tools designed to streamline machine learning workflows and ensure efficient deployment. These tools include:
| You will find later that each module of this workshop outlines details about our tool selection rationale and explores alternative options you may consider. |
-
OpenShift AI: OpenShift provides a robust Kubernetes-based platform for deploying containerized applications. OpenShift AI extends this by offering integrated tools for developing, training, and deploying AI models at scale. The platform’s GPU support enables high-performance model inference.
-
OpenShift Data Foundation: OpenShift Data Foundation (ODF) is a software-defined storage solution for OpenShift, providing block, file, and object storage for applications.
-
Roboflow: A tool for dataset management in computer vision projects. It provides image annotation, preprocessing, and augmentation.
-
Jupyter Notebook with Python: Jupyter Notebooks provide an interactive development environment, allowing participants to write and execute Python code seamlessly. This environment is essential for model experimentation, visualization, and iterative development.
-
YOLO Libraries: The workshop will leverage YOLO libraries (such as YOLOv11) to implement object detection. These libraries provide pre-trained models and tools to customize and fine tune the model for hardhat detection.
-
PyTorch Libraries: PyTorch provides the foundation for training and fine-tuning YOLO models. Its GPU acceleration and extensive ecosystem make it indispensable for building AI solutions.
-
GitHub Source Code Repository: Version control is critical for collaborative development. A Git repository will be used to manage the project codebase, track changes, and facilitate team collaboration.
-
Quay.io: A fully-managed hosted container image registry that offers both public and private repository options and automated lifecycle of your containerized artifacts, including advanced features such as replication or security scaning of images.
Workflow Overview
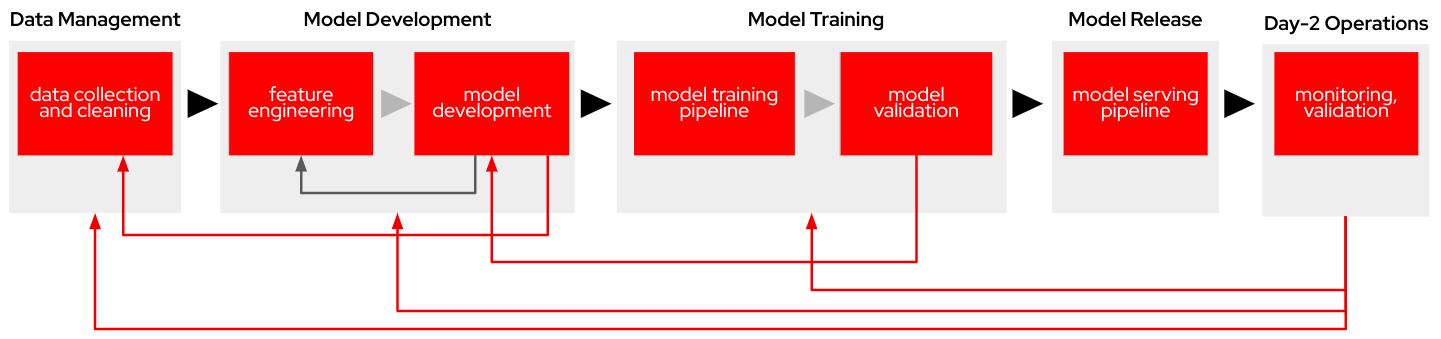
Find below the workflow that you will follow as AI specialist during the workshop (each of those will be a different "section").
-
Data Management: Data Collection and Cleaning, this is the foundational step where raw data is gathered, cleaned, and pre-processed to ensure quality and consistency. It serves as the input for downstream processes.
-
Model Development: Which includes the following steps:
-
Feature Engineering: Refined data is transformed into meaningful features that improve model performance. This phase often involves iterating back to the data collection step to enhance data quality.
-
Model Development: The core algorithms are designed and developed. This involves selecting and testing different model architectures. Iterations may occur, feeding back into feature engineering.
-
-
Model Training: With the following tasks:
-
Model Training Pipeline: The model is trained using the engineered features and developed algorithms, refining the weights and parameters based on the data.
-
Model Validation: The trained model is evaluated to ensure accuracy and robustness. If necessary, adjustments are made by looping back to the model development phase.
-
-
Model Serving: Model Serving Pipeline, after successful validation, the model is packaged and deployed into production environments, ready to handle stream or batch predictions.
-
Day-2 Operations: Monitoring and Validation: Post-deployment, the model’s performance is continuously monitored. This step ensures that the model maintains accuracy and adapts to data drift or operational changes. Monitoring may lead to re-initiating data collection, feature engineering, or retraining cycles to refine the model.
This won’t be a pure lineal workflow, you could find the need to step back to a previous step (feedback loops) in order to drive continuous improvement into the AI model creation, for example:
-
From monitoring directly back to data collection, ensuring updated datasets reflect operational realities.
-
From model validation to earlier phases (feature engineering and data collection) for iterative improvements.
-
From model serving back to model building for retraining based on performance metrics.
Now that you understand your requirements, your task and the workflow that you should follow, you can jump directly into the first section: Data Management.